Lymphoma Cancer Treatment in Lucknow
The best Lymphoma Cancer Treatment in Lucknow offers extremely high standard of medical care and ranks among some of the best hospitals in the world.
Book An Appointment
Types of Lymphoma
Non-Hodgkin lymphoma (NHL): Non-Hodgkin lymphoma (NHL) is the more common form of lymphoma. There are two types of lymphocytes – B lymphocytes and T lymphocytes. NHL develops mostly from B lymphocytes. They also do not show the presence of Reed-Sternberg cells. NHL can happen at any age and shows a non-contiguous spreading pattern.
Hodgkin lymphoma Hodgkin lymphoma (HL) is less common than Non-Hodgkin lymphoma (NHL) and is characterized by the presence of Reed-Sternberg cells seen under microscopy. HL essentially develops in a localized chain of lymph nodes. The cervical lymphatic chain is frequently involved (neck nodes), although it can also develop in the mesenteric and paraaortic chains. It spreads contiguously (from one node to another, or adjacent tissues) and rarely involves extra-nodal sites. HL also has a bimodal age distribution, generally differentiated into peak age groups of 15 to 34 years old, and those over 50 years.
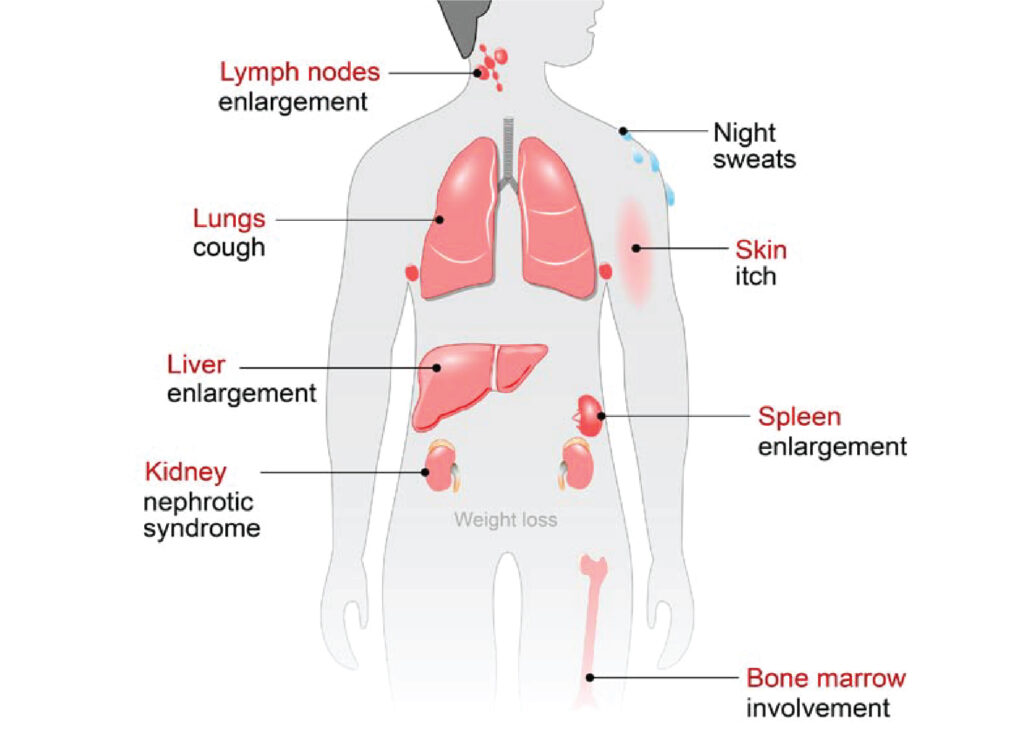
Symptoms of Lymphoma
The symptoms of both Hodgkin and non-Hodgkin lymphomas are:
- Painless swollen lymph nodes in the neck, under the arms, or in the groin
- Fever
- Night sweats
- Extreme fatigue
- Unexplained weight loss
- Difficulty getting over a common cold or an infection
- Anaemia
- Itching with or without a rash
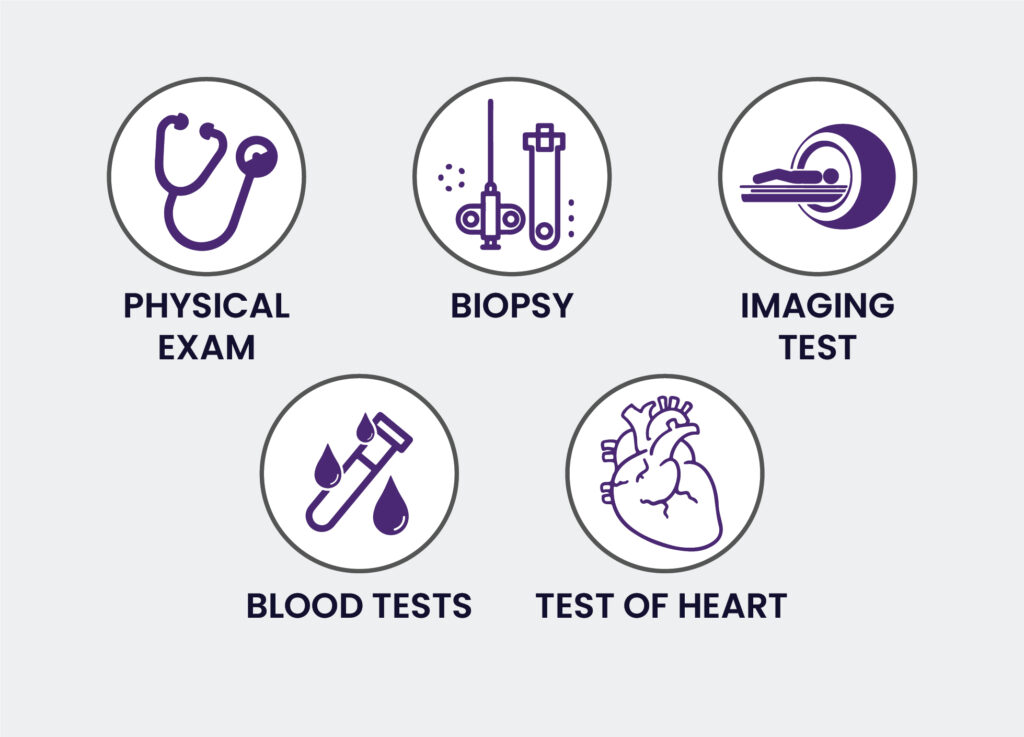
Lymphoma Diagnosis
In the initial stage, lymphoma cancer reveals symptoms of Leukemia. Thus, people tend to get confused. Hence, the doctor will ask to run a few tests which are helpful to diagnose the condition:
The diagnosis includes:
- A complete blood count (CBC) can be used to determine the levels of the platelet count or white blood cell count. If the levels are low, it may indicate that lymphoma is present in the bone marrow or blood.
- PET scan: A PET scan helps diagnose the lymph nodes. It produces 3D colored images which show the spread of lymphoma in the body. In addition, a PET scan highlights the affected areas in the body.
- MRI scan: The doctor will suggest running an MRI, which helps check the brain or spinal cord. It happens that cancer starts affecting other organs in the body. Thus, an MRI scan helps in revealing affected areas.
- Bone marrow biopsy: Bone marrow is more prone to be affected by the lymphocytes. Thus a biopsy is helpful for the same. In addition, the biopsy helps to check whether cancer has spread throughout the body.
- Gland biopsy: The gland biopsy is the most critical test every cancer patient has to go through. In this biopsy, the lymph nodes are diagnosed to find the affected parts
- CT scan: Apart from a PET scan and MRI, the doctor may ask to run a CT scan. It also helps in taking computed tomography photos of the internal organs.
Lymphoma Treatment
There are various management options available for Lymphoma, and it is treatable too. Lymphoma cancer Treatment In Lucknow conclude about the treatment method according to the Detection test report.
- Chemotherapy: This is an aggressive method in which drugs are given to kill the cancer cells, but they may also harm the healthy cells of the body.
- Radioimmunotherapy: In Radioimmunotherapy, high-powered radioactive doses are given to the body to kill the cancerous B-cells and C-cells.
- Steroids: Steroids are injected into the body to kill the cancer cells.
- Radiation Therapy: In Radiation Therapy, small patches of cancer-infected areas are taken and treated.
- Stem Cell Transplantation: Stem Cell Transplantation is used to restore the damaged/ infected bone marrow.
- Antibody Therapy:Antibody Therapy is the kind of therapy in which synthetic antibodies are inserted into the bloodstream to fight cancer agents.
- Biologic Therapy: It is one of the most suggested methods for Lymphoma treatment. In Biologic Therapy, living microorganisms are inserted into the body to stimulate the immune system to eliminate the cancer cells.
- Surgery: Surgery is also a good option to treat Lymphoma. Through the operation, the doctors remove cancer affects organs from the body
Why Choose Rudhir Arogya for Lymphoma Cancer Treatment Lucknow
With over 35 years of clinical experience, Rudhir Arogya Hematology Services Pvt. Ltd. is a trusted name in Lymphoma Cancer treatment Lucknow. Our patient-centric approach, combined with cutting-edge technology and a compassionate care team, makes us the preferred choice for individuals seeking treatment for aplastic anemia. We strive to offer affordable, efficient, and empathetic care, ensuring the best possible outcomes for our patients.

- Experienced Specialists
- Led by Dr. Sunil Dabadghao, our team has extensive expertise in treating various types of blood cancer, providing patients with confidence in their care.
- Comprehensive Care
- From diagnosis to treatment and follow-up, we offer a full spectrum of services to manage blood cancer effectively.
- Patient-Centric Approach
- We prioritize the needs and comfort of our patients, ensuring personalized and compassionate care throughout their treatment journey.
- Affordable Treatment Options
- We believe in making high-quality cancer care accessible, offering cost-effective treatment plans without compromising on quality.
For expert care and treatment at the leading Lymphoma hospital in Lucknow, contact Rudhir Arogya Hematology Services today. Our experienced team is here to guide you every step of the way.
Phone No : +91 8708700 48515
Email : info@rudhirarogya.com
Address: 4th Floor, Dr OP Chaudhary Hospital, Near SGPGI, Lucknow

